Suhan Gorya:

Fixed tabs display all items concurrently. To navigate to a different view, touch the tab, or swipe left or right.
Fixed tabs are displayed with equal width, based on the width of the widest tab label. If there is insufficient room to display all tabs, the tab labels themselves will be scrollable. For this reason, fixed tabs are best suited for displaying 3 or fewer tabs.


If view navigation is essential to your app, you can break out tabs into a separate action bar. This permits fast view switching even on narrower screens.
 Grid lists are an alternative to standard list views. They are best suited for showing data sets
that represent themselves through images. In contrast to simple lists, grid lists may scroll either
vertically or horizontally.
Grid lists are an alternative to standard list views. They are best suited for showing data sets
that represent themselves through images. In contrast to simple lists, grid lists may scroll either
vertically or horizontally.
The items in a grid list are arranged in two dimensions, one of which is fixed when scrolling content. The scrolling direction dictates the ordering of the items within the grid list. Since the scrolling direction is not deterministic, make it easy for the user to determine the orientation by cutting off grid items to communicate where the overflow is located.
Avoid creating grid lists that scroll in two dimensions.


Don't use scrolling tabs as a means to switch views in conjunction with horizontally scrolling grid lists, because the horizontal gesture for view and content navigation will conflict. If you show scrolling tabs for view navigation together with a grid list, use vertical grid scrolling for list navigation.
Use labels to display additional contextual information for your grid list items.
1. Tabs

Tabs in the action bar make it easy to explore and switch between different views or functional
aspects of your app, or to browse categorized data sets.
For details on using gestures to move between tabs, see the Swipe Views pattern.
Scrollable Tabs
Scrolling tab controls can contain a larger number of items than a standard tab control. To navigate
to the next/previous view, swipe left or right.
Scrolling tabs in the Play Store app.
Fixed Tabs
Fixed tabs display all items concurrently. To navigate to a different view, touch the tab, or swipe left or right.
Fixed tabs are displayed with equal width, based on the width of the widest tab label. If there is insufficient room to display all tabs, the tab labels themselves will be scrollable. For this reason, fixed tabs are best suited for displaying 3 or fewer tabs.

Tabs in Holo Dark & Light.

Tabs in the Google Play Movies app.
Stacked Tabs
If view navigation is essential to your app, you can break out tabs into a separate action bar. This permits fast view switching even on narrower screens.

Grid Lists

Grid View
Generic Grids
The items in a grid list are arranged in two dimensions, one of which is fixed when scrolling content. The scrolling direction dictates the ordering of the items within the grid list. Since the scrolling direction is not deterministic, make it easy for the user to determine the orientation by cutting off grid items to communicate where the overflow is located.
Avoid creating grid lists that scroll in two dimensions.

Vertical scrolling
Vertically scrolling grid list items are sorted in traditional western reading direction: left-to-right and top-down. When displaying the list, cut off the items in the bottom row to communicate that the user can scroll the list down to show additional items. Be sure to retain this scheme when the user rotates the screen.
Horizontal scrolling
Horizontally scrolling lists fix the vertical axis of the item grid. Compared to vertically scrolling lists, the sorting changes slightly to a top-down and left-to-right arrangement. Employ the same technique of cutting off the items in the rightmost column to indicate the scrolling direction.Don't use scrolling tabs as a means to switch views in conjunction with horizontally scrolling grid lists, because the horizontal gesture for view and content navigation will conflict. If you show scrolling tabs for view navigation together with a grid list, use vertical grid scrolling for list navigation.
Grid List with Labels
Use labels to display additional contextual information for your grid list items.

Style
Use semi-transparent panels on top of the grid list items to display your labels. This allows you to control the contrast and ensures legibility of the labels while letting the content "shine through".4. Scrolling
Scrolling allows the user to navigate to content in the overflow using a swipe gesture. The
scrolling speed is proportional to the speed of the gesture.
Appears during scrolling to indicate what portion of the content is currently in view.
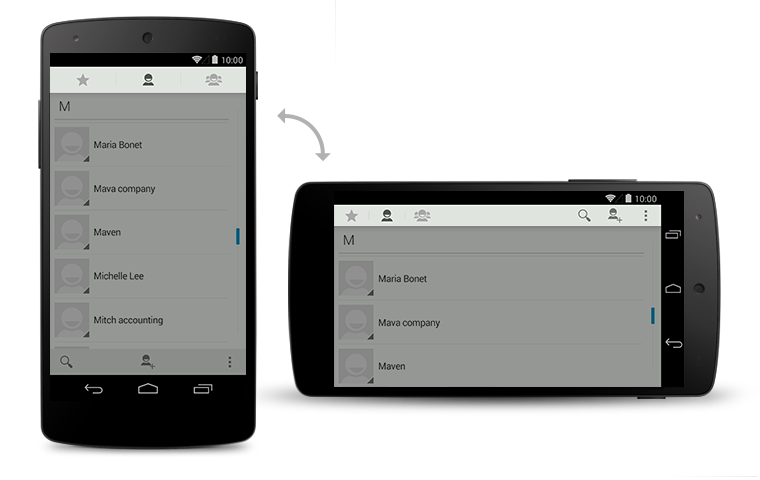
In addition to traditional scrolling, a long alphabetical list can also offer index scrolling: a way to quickly navigate to the items that begin with a particular letter. With index scrolling, a scroll indicator appears even when the user isn't scrolling. Touching or dragging it causes the current letter to pop up in a prominent way.
Scroll Indicator
Appears during scrolling to indicate what portion of the content is currently in view.
Index Scrolling
In addition to traditional scrolling, a long alphabetical list can also offer index scrolling: a way to quickly navigate to the items that begin with a particular letter. With index scrolling, a scroll indicator appears even when the user isn't scrolling. Touching or dragging it causes the current letter to pop up in a prominent way.






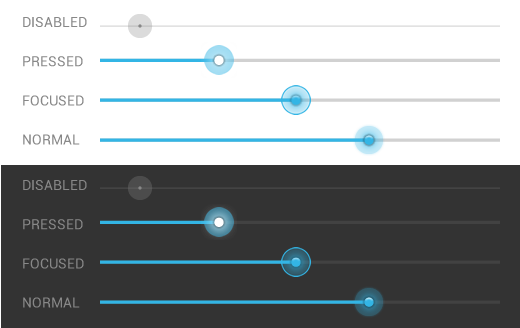
 A progress bar should always fill from 0% to 100% and never move
backwards to a lower value. If multiple operations are happening in
sequence, use the progress bar to represent the delay as a whole, so
that when the bar reaches 100%, it doesn't return back to 0%.
A progress bar should always fill from 0% to 100% and never move
backwards to a lower value. If multiple operations are happening in
sequence, use the progress bar to represent the delay as a whole, so
that when the bar reaches 100%, it doesn't return back to 0%.




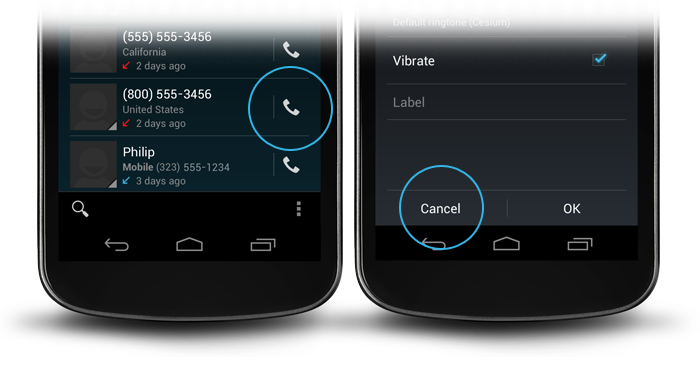
 The color indicates whether it's downloaded (blue) or not (gray). The
appearance of the pin indicates whether the download is permanent
(white, upright) or temporary (gray, diagonal). And when state is in the
process of changing, progress is indicated by a moving pie chart.
The color indicates whether it's downloaded (blue) or not (gray). The
appearance of the pin indicates whether the download is permanent
(white, upright) or temporary (gray, diagonal). And when state is in the
process of changing, progress is indicated by a moving pie chart.



No comments:
Post a Comment